Speciering Explained: The Role of Environmental Factors in Species Formation
The world around us is a mosaic of life. Every species, from the tiniest microbe to the largest mammal, plays a unique role in this intricate tapestry. But have you ever wondered how these diverse forms of life came to be? The process of speciering delves into this fascinating question. It invites us to explore how environmental factors shape and influence the formation of new species over time.
As we journey through different habitats—lush forests, arid deserts, or vibrant coral reefs—we can witness nature’s remarkable ability to adapt and evolve. Understanding speciering not only sheds light on biodiversity but also highlights how closely interconnected all living organisms are with their surroundings. Join us as we unravel the threads connecting environmental influences and the birth of new species in our evolving planet.
What is Speciering?
Speciering is a fascinating biological process that refers to the formation of new species. It captures the dynamic nature of life on Earth, where organisms adapt and change over time.
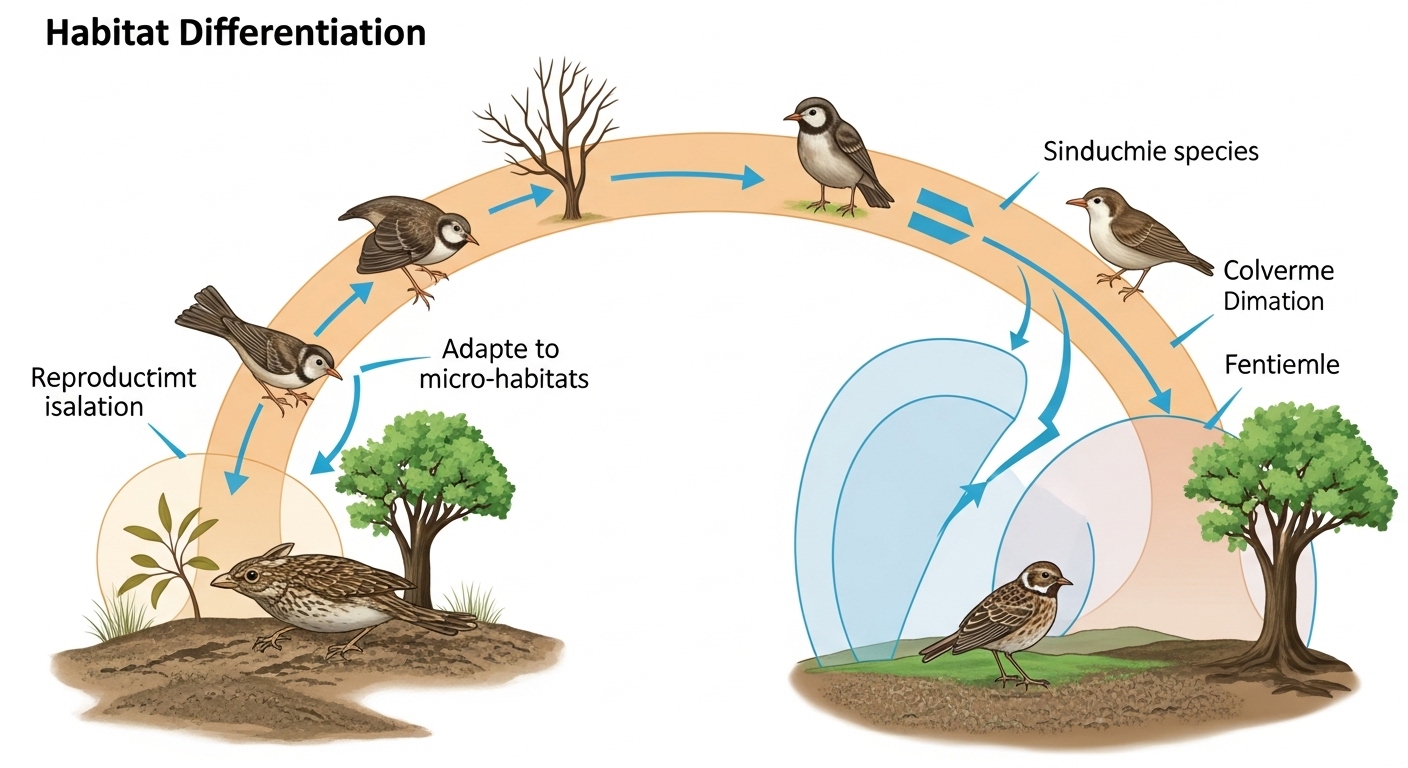
At its core, speciering occurs when populations become isolated from one another. This isolation can result from geographical barriers or ecological differences. As these groups evolve independently, they accumulate genetic changes.
These variations may lead to reproductive isolation, meaning members of different populations can no longer interbreed successfully. When this happens, distinct species emerge.
Understanding speciering opens up a window into evolutionary mechanisms at play in our ecosystems. It’s not just about genetics; it involves intricate interactions with environmental factors as well. Each unique path taken by a population tells a story of survival and adaptation within their specific habitats.
The Impact of Environmental Factors on Species Divergence
Environmental factors play a crucial role in species divergence. Changes in climate, habitat, and geography can lead to the isolation of populations. When groups are separated, they begin to evolve independently.
Variability in temperature and precipitation affects food sources and breeding patterns. Species adapting to different conditions may develop distinct traits over generations. This adaptation process fosters unique characteristics that define new species.
Barrier creation, such as mountains or rivers, also contributes significantly to divergence. These geographical features prevent gene flow between populations, leading them down separate evolutionary paths.
Moreover, ecological niches influence how species adapt over time. Different habitats create varied pressures that shape survival strategies. As these pressures differ across regions, the likelihood of speciation increases dramatically.
Environmental factors are fundamental forces driving the fascinating phenomenon of speciering within our planet’s biodiversity landscape.
Examples of Environmental Factors Affecting Species Formation
Environmental factors play a pivotal role in shaping the diversity of life on our planet. Climate is one such factor, influencing which species thrive in a given region. For instance, temperature fluctuations can lead to adaptations that foster survival.
Geographic barriers also contribute significantly to speciering. Mountains and rivers can isolate populations, creating distinct evolutionary paths over time. This isolation often results in unique traits emerging within each group.
Additionally, changes in habitat—like deforestation or urbanization—can prompt organisms to adapt or perish. Species may evolve new behaviors or physical characteristics as they respond to altered conditions.
Nutrient availability and soil types are equally influential. Plants adapting to different soils might develop various root systems, leading herbivores relying on them to follow suit with their own adaptations.
These examples illustrate how interconnected environmental variables generate the rich tapestry of life we observe today.
Evolutionary Processes Involved in Speciering
Speciering is a fascinating process that unfolds through various evolutionary mechanisms. One of the primary players in this drama is natural selection. As populations adapt to specific environments, traits advantageous for survival become more prominent over generations.
Genetic drift also plays a significant role, especially in smaller populations. Random changes can lead to distinct characteristics emerging within isolated groups. This divergence contributes to speciation as groups evolve independently.
Additionally, gene flow—the exchange of genes between populations—can impact speciation too. When barriers arise, such as geographical isolation or behavioral differences, gene flow diminishes and allows unique adaptations to take hold.
Mutation introduces new genetic variations into the mix. These mutations can provide raw material for evolution, paving the way for novel traits that might set species apart from their ancestors.
Together, these processes weave a complex tapestry of life where environmental pressures shape the emergence of new species over time.
The Controversy Surrounding the Concept of Speciering
The concept of speciering sparks vibrant debate among scientists. Some argue it’s a vital mechanism for understanding how species adapt and evolve over time. They emphasize its role in biodiversity.
Conversely, critics question whether speciering is an overly broad term. This skepticism stems from the complexity of evolution itself. Distinctions between species can blur, complicating clear definitions.
Another point of contention involves the impact of human activity on natural processes. Many believe that anthropogenic factors disrupt traditional pathways of speciation, creating new challenges for researchers to address.
Additionally, varying interpretations across disciplines add to the confusion surrounding speciering. Ecologists may view it through a different lens than geneticists or paleontologists. These differing perspectives highlight ongoing discussions in evolutionary biology today.
This controversy indicates that our understanding of life’s intricacies continues to evolve alongside scientific advancements and discoveries.
How Studying Speciering Can Aid in Conservation Efforts
Studying speciering provides critical insights into biodiversity. Understanding how new species emerge helps conservationists identify which ecosystems need protection.
As environments change, species often adapt or diverge. By studying these processes, we can pinpoint the factors driving this adaptation. This knowledge is vital for preserving vulnerable species facing habitat loss and climate change.
Moreover, identifying unique genetic traits in newly formed species allows for targeted conservation strategies. Protecting these distinct populations ensures that their contributions to ecological balance remain intact.
Research on speciering also informs restoration projects. By recognizing what makes certain habitats suitable for specific species, efforts can be tailored to enhance survival rates and promote healthy ecosystems.
In essence, the study of speciering equips us with a deeper understanding of life’s complexity and resilience, serving as a foundation for effective conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
Understanding speciering offers valuable insights into how species form and adapt over time. By examining the intricate relationship between environmental factors and species divergence, we can appreciate the complexity of life on Earth. From climate shifts to geographical barriers, these elements play a crucial role in shaping biodiversity.
The various evolutionary processes involved show us that speciering is not just a simple concept; it’s a dynamic phenomenon influenced by countless variables. The debates surrounding this topic highlight the ongoing quest for knowledge in biology, which continues to evolve.
Studying speciering isn’t just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications too. Conservation efforts benefit greatly from understanding how new species arise and why some may be at risk due to changing environments. As researchers delve deeper into these processes, they provide essential tools for protecting our planet’s diverse ecosystems.